NDIR vs Dual‑Beam NDIR vs Photoacoustic vs MOX CO₂ Sensors | VisiblAir Comparison Guide
Comprehensive Comparison: Top CO₂ Sensor Technologies
Effective indoor air quality monitoring starts with choosing the right CO₂ sensor. This guide covers:
- Fundamental principles behind NDIR, Dual‑Beam NDIR, Photoacoustic, and MOX sensors
- Comparative strengths, limitations, and cost implications
- Installation tips
1. Understanding NDIR (Non‑Dispersive Infrared) CO₂ Sensors
Operational principle:
An IR light beam travels through a gas chamber, where CO₂ molecules absorb specific wavelengths. A photodetector measures the drop in IR signal to determine concentration.
Why choose NDIR?
- Reliable accuracy (typically ± 50 ppm at 400–5,000 ppm)
- Stable output over long periods with proper calibration
- Affordable for schools, offices, homes, and greenhouses
How to optimize performance:
- Self-compensate for temperature/humidity with integrated sensors
- Clean sampling path regularly and calibrate every 1–2 years
- Enable auto-baseline correction overnight to adjust drift
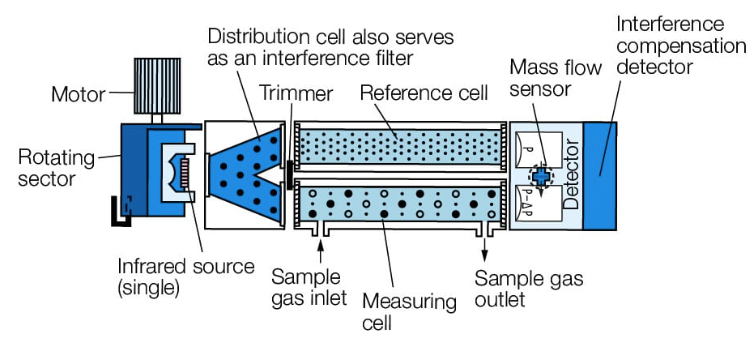
2. Dual‑Beam NDIR: The Precision Choice
How it improves accuracy:
- Uses two infrared sources and detectors—one measures sample gas, the other reference
- Differential reading cancels environmental drift and interference
Top advantages:
- Higher accuracy (± 30 ppm or better) in fluctuating conditions
- Virtually immune to humidity and pressure changes
- Low maintenance requirements—calibration every 2–3 years
3. Photoacoustic (PAS) Sensors: High Sensitivity in Compact Formats
How they work:
Light pulses (LED or laser) excite gas molecules, creating micropressure waves that are detected by a microphone and translated to CO₂ concentration.
Notable benefits:
- Ultra-high sensitivity, down to single-digit ppm levels
- Compact and efficient: perfect for portable air quality monitors or wearables
- Low power draw (< 200 mW) enables battery operation
Key considerations:
- Include humidity and pressure sensors for real-time compensation
- Require quarterly span calibration for optimal accuracy
4. MOX Sensors: When Not to Use Them for CO₂
Operating concept:
Gas molecules adsorb onto a heated metal‑oxide surface, changing its electrical resistance; however, this change isn’t selective to CO₂.
Why MOX falls short for CO₂ detection:
- Non-specific detection: responds to volatile compounds, humidity, combustion byproducts
- High drift and hysteresis: frequent baseline resets needed
- Poor accuracy: typically ± 100 ppm or more
🚫 Not recommended
Installation Best Practices
Mount sensors ~1–1.5 m above floor level, away from direct CO₂ sources (e.g. open windows or HVAC mouths).
Comparison Table
| Sensor Type | Accuracy | Calibration Interval |
|---|---|---|
| NDIR | ± 50 ppm | 12–24 months |
| Dual‑Beam NDIR | ± 30 ppm or better | 24–36 months |
| Photoacoustic (PAS) | < 10 ppm (very sensitive) | Quarterly or semi‑annual |
| MOX | ± 100 ppm+ | Weekly resets |
Drive Better Air with VisiblAir
Explore our range of NDIR, Dual‑Beam NDIR, and Photoacoustic sensors—each optimized for accuracy, power efficiency, and durability:
👉 VisiblAir CO₂ Sensor Collection
Improve decision-making, energy efficiency and indoor comfort with actionable air quality insights.